If you own a lionhead rabbit or have seen one, you know about this rabbit family: they are cute and unique bunnies. Their fluffy manes and tiny ears make these rabbits look like small lions jumping around. But have you ever noticed the ear structure of the Lionhead rabbit and what function or benefits they get from their short lop ear?
In this blog, we discuss the structure of the Lionhead rabbit’s ears, explain why their ears are special, and discuss how to care for your bunny friend.
- What Makes Lionhead Rabbit Ears Structure Unique?
- Why Are Lionhead Rabbit's Ears So Short?
- The Anatomy of a Lionhead Rabbit's Ear Structure:
- Lionhead Rabbit Ear Structure and Their Functions:
- Lionhead Rabbit Ear Structure Diagram:
- Lionhead Rabbit Ear Positioning Pictures:
- Why Ear Care is Crucial for Lionhead:
- Step-by-Step Guide to Caring for Your Lionhead Rabbit's Ears:
- The Observation of a Lionhead Rabbit owner:
- Frequently Asked Questions:
What Makes Lionhead Rabbit Ears Structure Unique?
The lionhead rabbit’s ears are as interesting as those of larger rabbit breeds, like the silver fox rabbit. Lionhead rabbits have short, upright ears that are perfect for their tiny size. Their ears are naturally around 2 to 3 inches long and straight up, which indicates their curious and alert personality.
The floppy and up-eared rabbit breed has three interlocking parts of cartilage that keep its ears upright. Still, lionheads, as lop-ear rabbits, have a gap between the cartilage, which prevents them from keeping their ears upright.
Lionhead rabbits’ ear specialty allows them to rotate their ears up to 270 degrees and capture sound frequencies up to 42,000 Hz. This frequency range exceeds a human being’s sound-hearing ability of 20,000 Hz.
Why Are Lionhead Rabbit’s Ears So Short?
The Lionhead rabbit ear structure is a result of selective breeding. The breeder tried to create a rabbit breed that is easy to care for and handle as a pet friend and also should be cute, adorable, and unique, and the result they created the lionhead rabbit breed, a small rabbit family with a short ear structure because the shorter ears rabbits are less prone to injuries and ear infections compared to the long floppy ear breeds. With small size and short ear structure, Lionhead rabbits are a remarkable choice for new rabbit owners.
The Anatomy of a Lionhead Rabbit’s Ear Structure:
Lionhead rabbits are known for their short lop ear and remarkable hearing sense, which play a crucial role in their lives. Lionhead rabbits use their ears for communication, behavior, and environmental interaction.
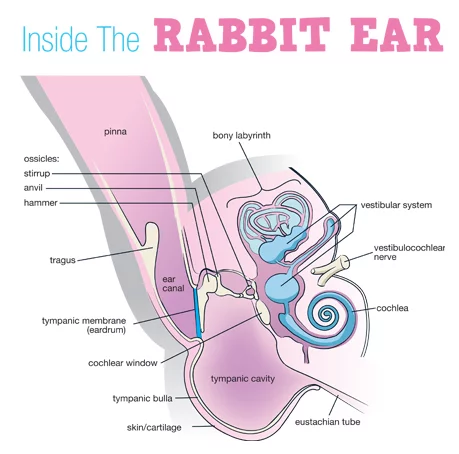
Outer Ear (Pinna):
This part is the visible area of the ear. The Lionhead rabbit’s pinna is short and covered in soft fur, which helps it receive sound waves and transmit them into the ear canal.
Furthermore, the pinna has a relatively large blood process, and the extensive system of blood vessels manages a lot of surface area for heat abstract. When the rabbit gets overheated, the outer ear performs a major role in controlling the temperature system.
Middle Ear of Rabbit:
The middle ear, located in the rabbit’s skull’s back centre, contains tiny bones (ossicles) that amplify sound. This part of the rabbit vibrates when sound hits it and protects the eardrum from harm.
Inner Ear of Rabbit:
This area of the rabbit ear contains two parts: the cochlea and the spiral-shaped tube; these parts of the inner ear convert sound waves into signals and transmit them to the rabbit’s brain to understand the nature of sound. The inner ear of rabbits also helps to balance their activities, so that’s why rabbits are fast-moving and excellent jumpers.
Lionhead Rabbit Ear Structure and Their Functions:
The Lionhead rabbit ear structure is not just about beautiful looks; it performs a vital role in their survival.
The Hearing Ability of Lionhead Rabbit:
Despite their small size, Lionhead rabbit ears are incredibly functional. This breed’s ears are brilliantly sensitive and can detect the faintest sound. Lion-head rabbits’ astute hearing ability helps them recognize potential danger and save themselves from it at the perfect time. Because rabbits are prey animals, their astute hearing ability is their main line of defence against their predators.
So we can say that their unique hearing ability guarantees their perfect secure living environment, and they enjoy it,
Lionhead Ears for Communication:
Rabbits also use their ears to communicate their emotions; upright ears mean they are curious about something, while flattened ears indicate aggression or danger. Therefore, to understand these various positions of rabbits’ ears. The rabbit’s owners can realize their rabbit’s behaviour and social dynamics.
Rabbit Ears for Regulating Temperature:
The Lionhead rabbit’s shorter ears play a significant role in regulating body temperature. These bunnies’ ears include a system of blood vessels that helps maintain heat. On summer days, these blood vessels expand to reduce the extra heat from the body, while in the winter season, they maintain body warmth.
Lionhead Rabbit Ear Structure Diagram:
A Lionhead rabbit ear structure diagram can be invaluable for visual learners. These diagrams show the different parts of the ear, including the pinna, ear canal, and inner ear. You can find detailed diagrams in veterinary guides or online resources.
Thanks to a picture taken from www.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Lionhead Rabbit Ear Positioning Pictures:
Sometimes, a picture is worth a thousand words. Lionhead rabbit ear position pictures can help you identify healthy ears and spot potential problems. Look for clear, high-quality images that show the ear’s shape, fur coverage.















Why Ear Care is Crucial for Lionhead:
Even though Lionhead rabbits have shorter ears, they still need proper care. Here’s why:
- Preventing from Infections: Rabbit ears are sensitive and can easily get infected if not cleaned regularly. Ear mites, wax buildup, and bacteria can cause serious problems.
- Maintaining Hearing: A healthy ear structure ensures your rabbit can hear well, which is essential for their safety and well-being.
- Comfort level: Clean ears mean a happy bunny! If your rabbit’s ears are itchy or painful, they’ll be stressed and uncomfortable.
Step-by-Step Guide to Caring for Your Lionhead Rabbit’s Ears:
Now that you know how critical ear care is, let’s walk through the steps to keep your Lionhead rabbit’s ears in excellent shape.
Step 1: Regular Checkups
- What to Do: you should inspect your rabbit’s ears once a week. Carefully look for redness, swelling, or any other changes in the ear to prevent serious issues.
2: Cleaning the Rabbit Ears
- You Need: To clean your rabbit ears, use a soft cloth, cotton balls, and a rabbit-safe ear cleaner.
- How to Do It: Dampen the cloth or cotton ball with the cleaner and gently wipe the inside of the ear. Avoid going too deep to prevent injury. Please do not rely on Q-tips or harsh chemicals, as they can damage the delicate ear structure.
3: Watch for Signs of Trouble
- What to Look For: Scratching, head tilting, or a foul odour are signs of ear problems. If you notice any indication, immediately take your rabbit to a vet.
4: Provide a Clean Environment
- Why It Matters: A clean living space reduces the risk of infections. Make sure your rabbit’s cage is free of dust and debris.

The Observation of a Lionhead Rabbit owner:
As a pet rabbit lover, the first time I bought my lionhead rabbit for home, I was amazed by its cuteness, body structure, and incredibly expressive ears.
After some days, I noticed it shaking its head and twitching its ears. At first, I thought it was because of his natural behavior, but after observing deeply, I realized my rabbit was trying to locate the sound of a bird outside my home.
So, at that moment, I appreciated the incredible lionhead rabbit ear structure, which is not only for a cute look but also for communication and the survival of life for them.

Frequently Asked Questions:
Lionhead rabbits ideally do not have floppy ears. But they have upright and straight ears. Usually, their ears are erect and proportionate with their body size.
However, some Lionhead rabbits have floppy ears because of crossbreeding with lop-eared rabbit breeds.
A healthy rabbit’s ears should have the following characteristics:
Upright or Breed-Specific Shape: Like Lionhead rabbits, most rabbit breeds have upright or straight ears, but some other rabbit families like floppy ears that hang down. Remember, the ear shape always aligns with the breed’s characteristics.
Clean and Free of Discharge: Check your pet friend’s ears. The rabbit’s ears are healthy, with no indication of wax buildup or redness. Smelly or dirty ears indicate an ear infection.
Good Blood Flow and Temperature: The rabbit’s ear also works as a vascular system that helps regulate body temperature. Rabbit ears maintain good blood flow for body temperature regulation in hot and cold environments.
No Swelling or Lumps: The rabbit ears should not have any swelling or scabs as these signs indicate injury or disease.
Active Movement: Rabbits use their ears to express emotions and listen for sounds. They should move their ears frequently in response to noises or their environment.
Rabbits, including Lionheads, exhibit specific behaviours and body language when happy and content. Here are some signs to look for:
Binkying: when the rabbit jumps into the air and twists its body or head. That is a clear sign of joy and excitement.
Flopping: When your pet friend rabbit flops onto its side or back, which indicates it feels safe and relaxed in its environment.
Purring: Rabbits purr by gently grinding their teeth, which is a sign of contentment. This action often happens when you give them food, or they are comfortable.
Relaxed Body Language: When rabbit ears are in a neutral position, like not pinned back, and eyes are half-closed or bright and alert, that means your rabbit is in a happy and relaxed position.







